Laboratory Animal Models 3D Cultures And Organoids. Derived from stem cells, organoids can be expanded to a wide range of tissue types including liver, lung, brain, kidney, stomach, and. Medical research in the recent years has achieved significant progress due to the increasing prominence of organoid technology.
By reproducing important parameters of the in vivo environment, 3d models can provide unique insight into the behavior of stem cells and developing tissues in vitro. Current 3d cardiac organoid cultures have shown their utility in modelling key developmental. Moreover, these 3d cultures have been considered more realistic and reduce the average number of animals in experimentation.
Join Leading Researchers In The Field And Publish With Us.
Various developed tissue organoids bridge the limitations of conventional 2d cell culture and animal models by recapitulating in vivo cellular complexity. “organoids therefore bridge the gap between in vitro cell cultures and living animal models.” the organoid technology has been getting a lot of attention from numerous research groups around the world because of the potential it has. Organoids can be generated directly from patient tissue or laboratory animal tissue for most epithelial organs (hub organoids™), including both healthy and diseased intestine, liver, pancreas, breast, and lung or through the directed differentiation of pluripotent and embryonic stem cells.
These Data Suggest That Our Established 2.5D Organoid Culture Method Might Become A Reasonable And Useful Tool Instead Of 3D Organoids In Dog Bc Research And Therapy.
Join leading researchers in the field and publish with us. Utilizing organoids to study breast cancer. Furthermore, the advent of 3d cultures made possible the development of disease and tissue models that can be used to substitute or, at least, to contribute with studies using traditional animal models in research.
And Significantly Reduce Reliance On Animal Models.
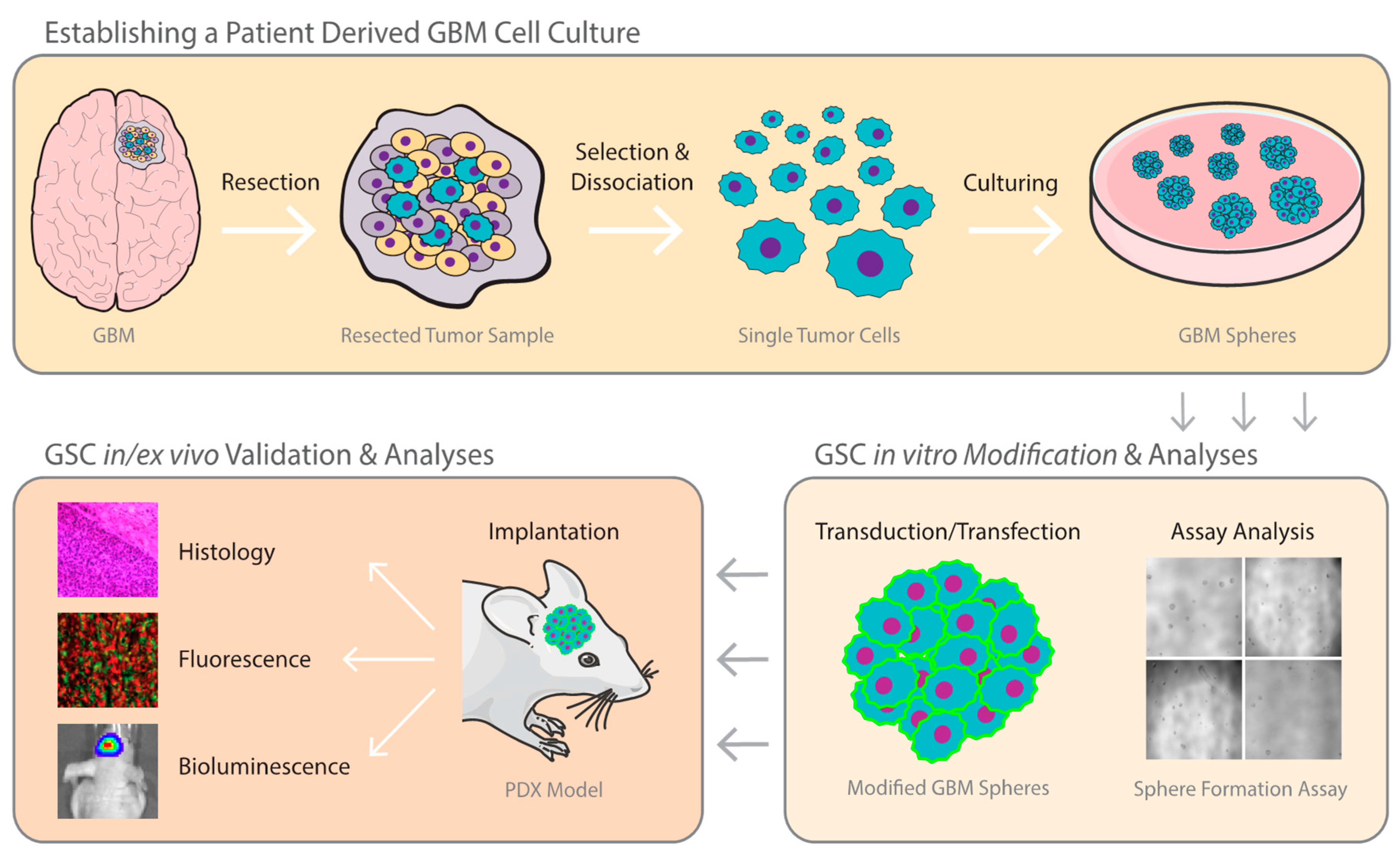
Medical research in the recent years has achieved significant progress due to the increasing prominence of organoid technology. The advent of 3d models could constitute an important step forward in cancer research, filling the gap between traditional cell cultures and animal models (fig. Derived from stem cells, organoids can be expanded to a wide range of tissue types including liver, lung, brain, kidney, stomach, and.
We Highlight The Most Recent Advances In Developing In Vitro 3D Models And Introduce The Potential Of Lung Organoids As A New Tool To Study Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection.
A comprehensive overview of the global markets for laboratory animal models, 3d cell cultures and organoids. These 3d cultures have advantages over both 2d cultures and in vivo animal models. Their growing importance in various fields of research saw them named ‘method of the year 2017’ 1 and their use in drug testing has seen a large increase in the market for 3d cell cultures.
As Such, Researchers Have Created Physiologically Relevant Organoid Models For Many Organs.
Moreover, these 3d cultures have been considered more realistic and reduce the average number of animals in experimentation. Various developed tissue organoids bridge the limitations of conventional 2d cell culture and animal models by recapitulating in vivo cellular complexity. The substrate selected to culture and grow spheroids or organoids is a vital aspect in obtaining reproducible 3d cancer cell models.
0 Comments